

"As long as you don't get that secondary bacteriological infection it should go away on its own over time," he added.Īffected lakes and ponds typically have signage posted warning people of infected waters, but Harker said to check local health department websites for active warnings before you head out. If you do find yourself with the rash, Harker said over the counter anti-itch lotions and avoiding scratching are the best ways to treat it. "Or even better if you can shower right afterwards those things can help prevent it." "At least towel dry afterwards," he said. Read - Utah park warns of visitors experiencing 'Swimmer's Itch' Harker recommends taking a few steps any time you swim in a shallow body of water. The best way to avoid swimmer's itch is to avoid swimming in affected lakes or ponds, but it can be difficult for the state to keep on top of which bodies of water have active infestations. "If you were to scratch it and you were to get a secondary bacterial infection as a result of that, then that could be something you might need to get medical attention for," Harker said. The bacteria can develop in any hot tub but is most common in wooden tubs.
#Heat rash vs swimmers itch skin
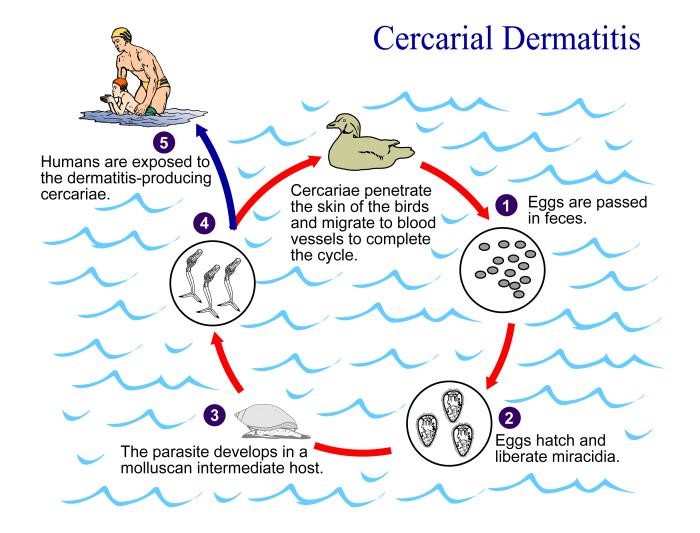
He added that the parasite and rash themselves are typically not harmful to humans, but it's best to avoid touching or scratching the rash as it could lead to bigger problems. Hot tub rash or folliculitis is a skin infection caused by certain bacteria thriving in warm, wet areas. "You hear different reports of small reddish pimples, small blisters, tingling, burning, and itching of the skin," Harker said, The bird passes the parasite's eggs through its feces, and it is then consumed by water snails, which again passes them through its feces and the mature parasite can then burrow in the skin causing an allergic reaction ranging from mild to severe. Read - Lifeguards honored for lifesaving rescue at Payson pool "It's looking for a different host than humans, but if humans are there then it can burrow into the skin causing that rash which itches, thus swimmer's itch," Harker added. Swimmer's itch is caused by a microscopic parasite found in many water birds. "Hot temperatures and shallow waters seem to increase the likelihood of it," he said. The Bear River Health Department is asking the public to avoid swimming in the Mantua Reservoir and 'The Pond' at Willard Bay.īen Harker with the Bear River Health Department said the extreme heat and drought impacting 98 percent of the state could be a contributing factor to an increase in infestations. The parasite that causes the rash can be more prevalent during times of high heat and drought. 13, 2021.SALT LAKE CITY - One local health department is warning residents of swimmer's itch infestation at two northern Utah lakes and ponds.
In: Taylor and Kelly's Dermatology for Skin of Color. Exanthematous (maculopapular) drug eruption. Drug hypersensitivity: Classification and clinical features. Health Education & Content Services (Patient Education).Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Parasites: Cercarial dermatitis (also known as swimmer's itch).American Osteopathic College of Dermatology. In adults, miliaria often affects the upper trunk, scalp, neck and flexures. In children, miliaria involves the trunk and the skin folds of the neck, axilla or groin.

In: Taylor and Kelly's Dermatology for Skin of Color. Miliaria rubra, the most common form of heat rash, results in red, 24 mm, non- follicular papules and papulovesicles.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
